

September 30, 2021
[ IP News-Design/Trademark ]
Do you know that there is a way to obtain both patent and design rights from one patent application in Japan?
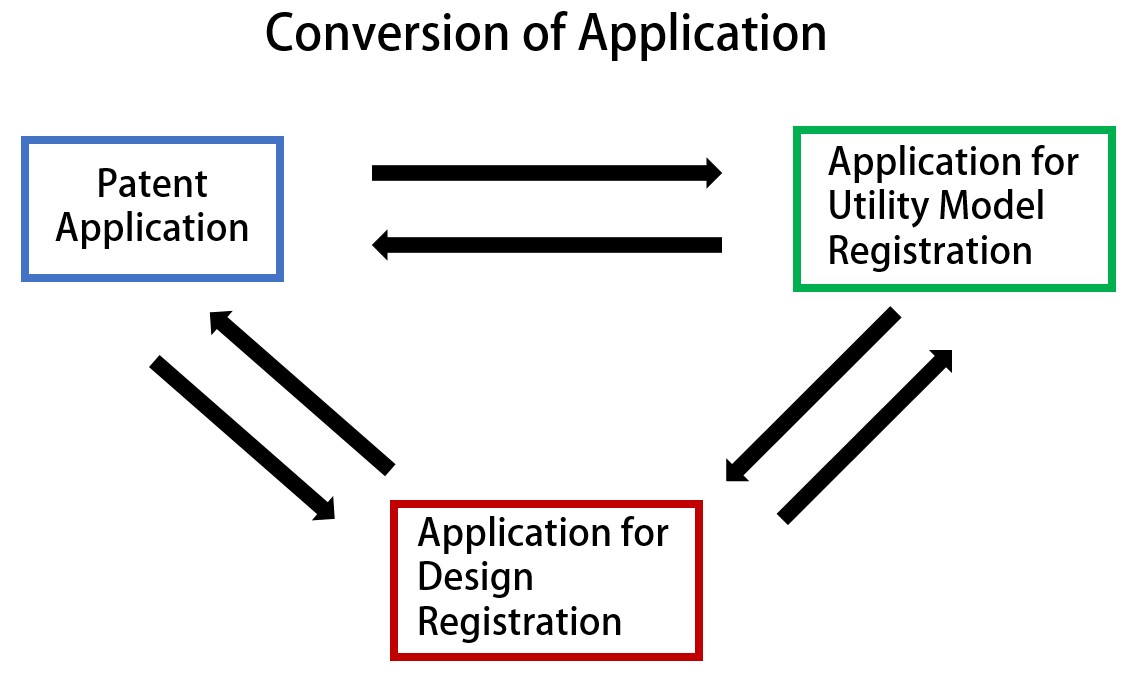
Do you know a conversion application system in Japan? In Japan, a patent application can be converted into an application for utility model registration or an application for design registration, an application for utility model registration can be converted into a patent application or an application for design registration, and an application for design registration can be converted into a patent application or an application for utility model registration (Patent Act Article 46, Utility Model Law Article 10, Design Law Article 13).
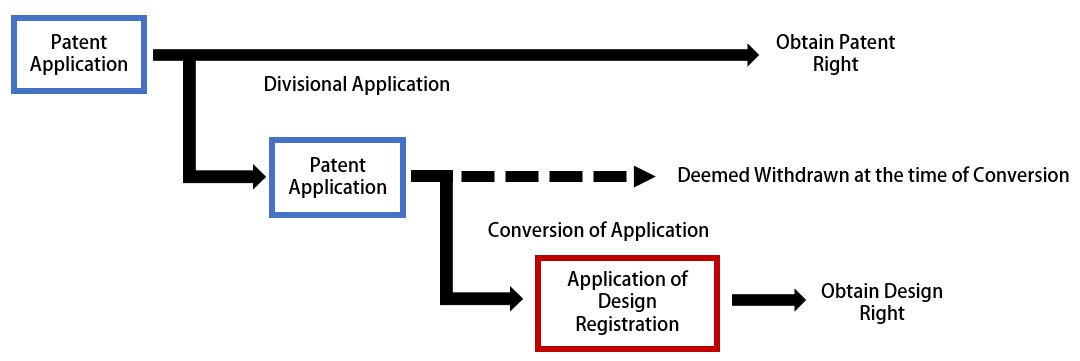
When an application is converted, the original application shall be deemed to have been withdrawn. For example, if a patent application is converted into an application for design registration, the original patent application shall be deemed to have been withdrawn. However, by using the conversion application system and a divisional application system in combination, the right of the original application is also obtainable.
For example, one can file a divisional application from a patent application, and the divisional application is converted into an application for design registration. In this case, the divisional patent application is deemed to have been withdrawn at the time of the conversion into the application of design registration; however, the original patent application can remain pending for examination, making it possible to obtain rights for both the patent application and the application for design registration.
The specific requirements for the conversion of a patent application into a design registration application (i.e., the specific requirements for the converted design registration application to be deemed to have been filed at the same time as the original patent application) are as follows.
(A) The design of the new application for design registration after the conversion must be specifically described in the original specification and drawings of the original patent application so as to be clearly recognized.
(B) The design of the new application for design registration after the conversion is identical to the design represented in the original specification and drawings of the original patent application.
It is important to note that the new application for design registration after the conversion not only allows the applicant to obtain a design registration that is completely identical to the drawings disclosed in the original patent application, but also allows the applicant to obtain a design registration that can be comprehensively grasped from the drawings and the specification of the original patent application. What is also noticeable is that in some cases, it is possible to obtain a design registration for a design that is represented in a part of the drawings disclosed in the original patent application.
The following are some examples of applications that have been accepted as the conversion of application.
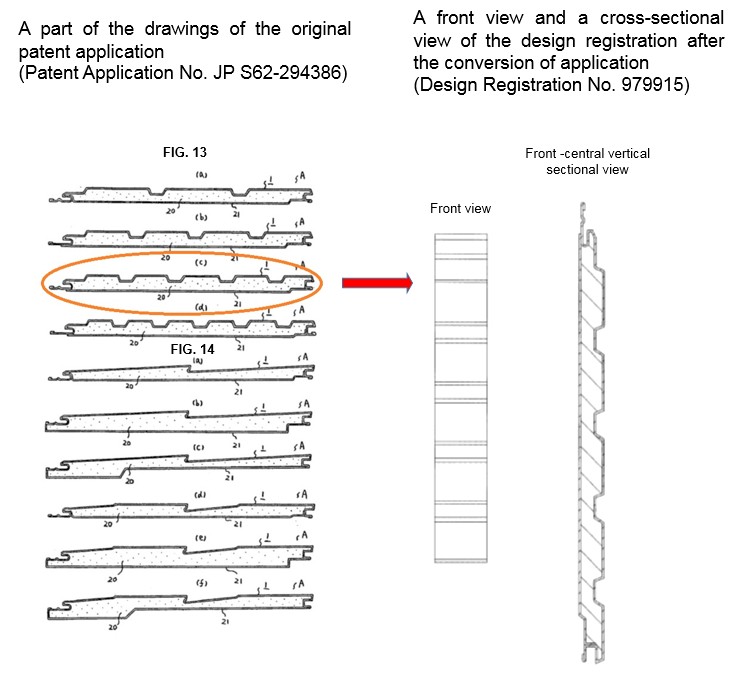
(1) Invalidation 2009-880001
The design registration in this case was a patent application for siding board that is an exterior wall material forming an exterior wall of a building. This patent application was divided into a divisional application and the divisional application was converted into an application for design registration.
In this case, the appellant who claimed invalidation of the design registration stated that “the registered design was invalid because it was based on the conversion of the patent application into a design application on the basis of only one cross-sectional view included in the original patent application, and the original patent application does not specifically describe the registered design”.
However, in the decision of this case, it was determined that when the description of the specification was taken into consideration in addition to the drawings of the original patent application, the design according to the design registration in this case can be recognized as being specifically described in the application document of the original patent application so as to be clearly and sufficiently recognized.
(2) Appeal No. 2009-2816
The application in this case was originally a patent application for a multimedia playback device. Then, this application was divided into a divisional application, and the divisional application was converted into an application for design registration based on a part of a screen of the playback device disclosed in the drawings of the original application, and the design application was registered.
In this case, at the examination stage where the examiner determines whether the application could be registered or not, the examiner determined that the conversion of the application was not lawfully done since the contents of a menu screen disclosed in FIG. 3 of the original patent application were not the same as the contents of a front view in the application for design registration.
However, in an appeal against the decision of refusal filed by the applicant who was dissatisfied with the decision, it was determined that the design registration was acceptable since the conversion of application into a design application was lawfully done when considering the entire application documents of the original patent application.
A part of the drawings of the original patent application
(Patent Application No. JP2003-149924)
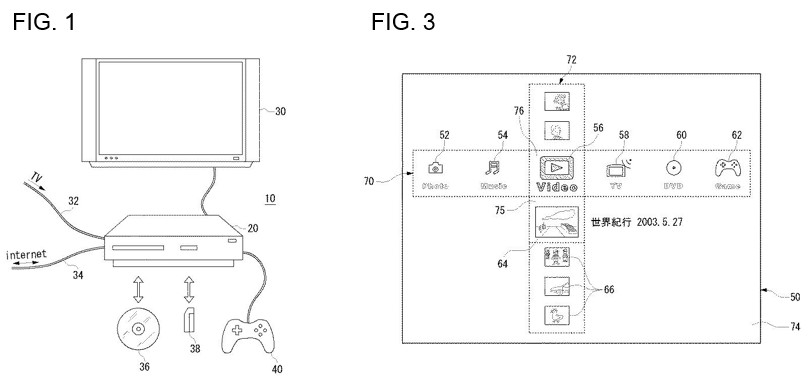
A partial enlarged front view of the design registration after the conversion of application (Design Registration No. 1380985)
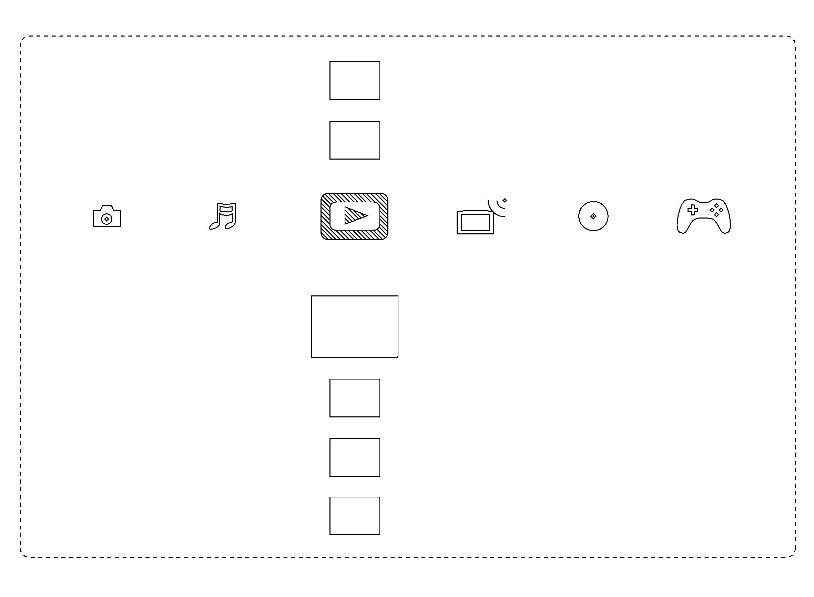
(3) Appeal No. 2006-26021
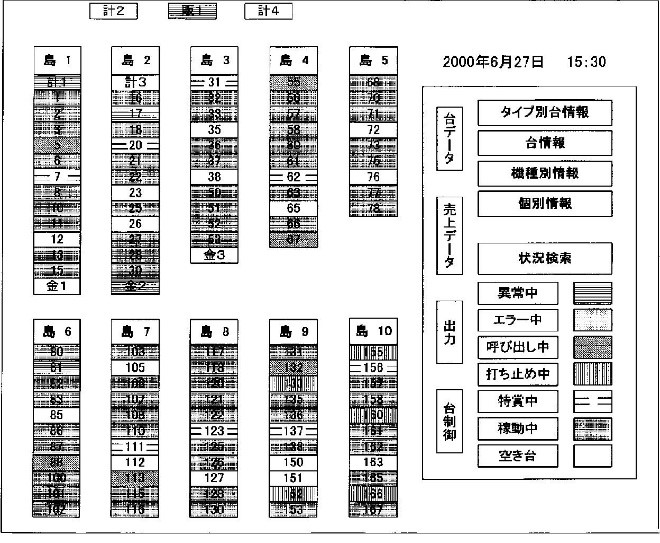
The application in this case was originally a patent application for a management device to display a game status of pachinko machines, slot machines, and other amusement machines to users. This application was divided into a divisional application and the divisional application was converted into an application for design registration as a partial design for a part of a screen of the management device disclosed in the drawings of the patent application.
In the examination stage, the examiner determined that the conversion of application was not lawfully done due to failure to satisfy the requirements for the conversion of application. That is, the partial design must be disclosed in the description of the original patent application in a manner enabling it to be distinguished from other parts, in addition to the fact that the original patent application contains the design (partial design).
In the trial stage where the applicant appealed against the examiner’s decision, the above decision in the examination stage was overturned. The appeal examiner determined that the conversion of application was lawfully done since the applicant was allowed to freely choose a part of the design as a subject partial design if the patent application included an image related to the application for design registration.
A part of the drawings of the original patent application
(Patent Application No. 2005-133346)
Figure 14.
A part of the drawings of the design registration after the conversion of application
(Design Registration No. 1304530)
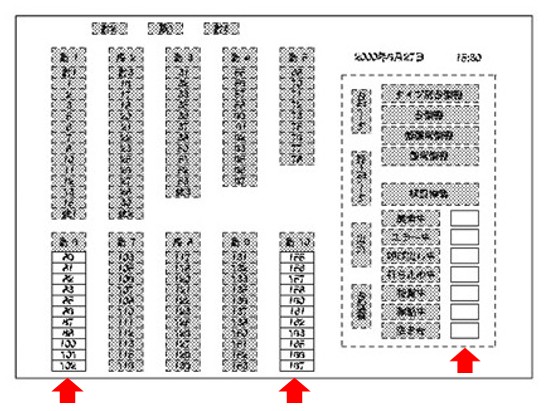
The solid-line portions pointed by red arrows, in other words, the solid-line frame portions are the subject design to register as a partial design in this case. In the figure, the red arrows were added by our firm to clarify the locations of the solid-line portions. Here, letters inside the solid lines are indicated by dashed lines, and thus, they are not considered as portions to be registered.
If an application is converted, as described in this article, the converted application is advantageously deemed to have been filed at the same time as the original patent application.
However, timing requirements for filing a conversion application will vary depending on the examination status of the original application and other factors.
In addition, when one converts an application, which claims priority, into an application for design registration, attention must be paid for an applicable priority period. Under the Paris Convention, the priority period is set for 12 months in relation to patent applications and utility model applications, and for 6 months in relation to design registration applications. If the original patent application filed with the Japan Patent Office was filed within 12 months from the filing date of the patent application in a first country (first foreign application), the priority claim based on the first foreign application will naturally be legally recognized if the original patent application remains as a patent application. However, when the original patent application is converted into an application for design registration and the original patent application was filed after 6 months and before 12 months from the filing date of the first foreign application, the application is deemed to be filed in Japan after 6 months from the filing date of the first foreign application (i.e., after the expiration of the 6 months priority period set for design registration applications under the Paris Convention). Therefore, the priority claim would not be effective for the converted application, and the novelty will be judged based on the filing date of the original patent application.
In this article, we introduced several cases where the conversion into various design registration applications were possible if the original application documents includes the descriptions on the design. However, it depends on the case, and it may be necessary to use the expertise of a specialist to determine whether or not the invention that you wish to obtain rights would be suitable/acceptable for the conversion of application.
Therefore, please feel free to contact us if you would like to obtain further advice and suggestions to file the conversion of application in Japan.
Edited by Rieko Yoshimoto